| Author: Ashish Kumar | Published: 29-Jan-2026 |
Choosing the right cloud service providers can be tough. Prices, tools, and coverage differ. Your decision shapes cost, speed, and growth.
Cloud spending hit over 100 billion dollars in Q2 2025. Most went to AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These three top cloud service providers hold most of the market.
This guide helps you compare cloud providers. You will see which one fits your needs best.
Why the choice of cloud providers matters
Choosing the right cloud provider is no longer just a technical decision; it’s a business-critical strategy. The provider you select directly affects your cost structure, performance, security posture, scalability, and customer experience.
As per Teleglobal research cloud provider can reduce your operational costs by up to 15-30% through optimized pricing models, automated scaling, and efficient resource allocation.
On the other hand, a poor provider choice results in:
- Higher downtime, costing enterprises an average of $5,600 per minute
- Unexpected billing spikes, especially with unmanaged storage, data egress, and compute
- Security vulnerabilities leading to massive financial and reputation damage
Different Types of Cloud Providers and Their Impact
1. Cloud Service Providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
Cloud service providers run your applications, services, and databases.
Their capabilities determine:
- Application uptime (AWS offers 99.99% SLA for many services)
- Global reach (Azure operates in 60+ regions)
- AI/ML adoption speed (Google Cloud leads in data & AI tools)
Business Impact:
Faster applications → higher user satisfaction → better conversion rates.
2. Cloud Storage Providers (S3, Azure Blob, Google Cloud Storage)
- Cloud storage providers control where your files live.
- Cloud hosting providers power your websites and servers.
Business Impact:
Secure storage prevents data loss and supports compliance-heavy industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
3. Cloud Hosting Providers (AWS EC2, AKS, Google Compute Engine)
These providers power websites, APIs, and virtual servers.
Providers differ in:
- Compute speed
- Network latency
- Traffic handling capability
- Auto-scaling support
Business Impact:
A slow or unreliable hosting provider leads to lower SEO ranking, poor user experience, and lost revenue during peak traffic.
The Provider You Choose Also Impacts:
- Security posture — shared responsibility model
- Compliance success — certifications vary by region
- Disaster recovery time — multi-region capability matters
- User experience — low latency and high throughput = better product adoption
Key Factors to Compare When Choosing a Cloud Provider
Selecting a cloud provider should be a strategic business decisionthat directly impacts performance, cost efficiency, compliance, and long-term scalability. According to the Flexera 2024 Cloud Report, 89% of enterprises use multiple cloud providers, and 57% use multi-cloud FinOps tools. evaluating providers with a structured framework has become essential.
Below are the key factors every organization must compare before committing to AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or any other cloud platform.
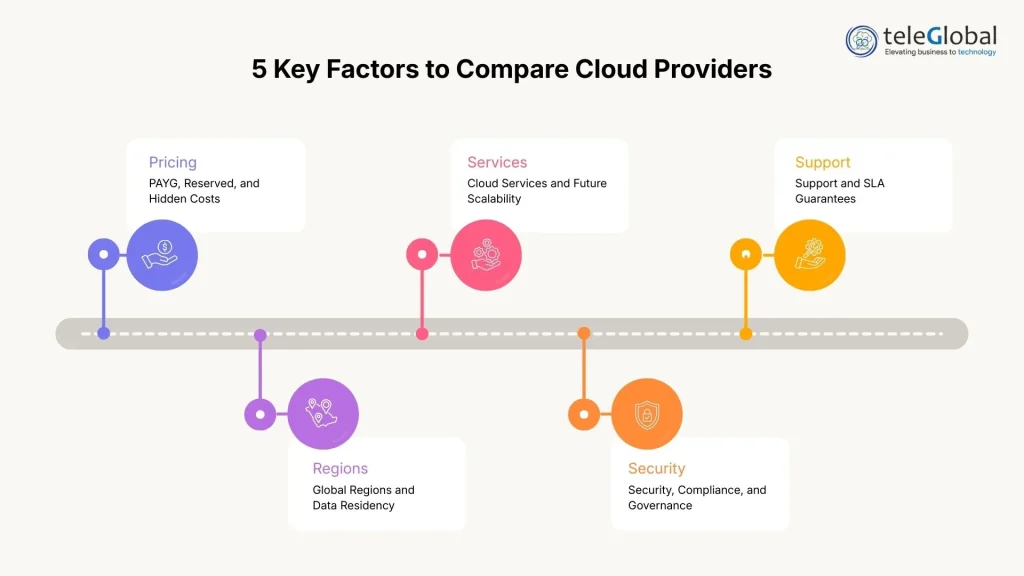
Pricing
Cloud pricing models vary significantly across providers, and understanding them is critical for managing long-term costs.
Businesses should compare:
- Pay-As-You-Go (On-Demand) pricing for flexible workloads
- Reserved or Long-Term Commitments (1–3 years) for predictable workloads
- Spot/Preemptible Instances, which can be up to 90% cheaper
- Data egress charges, which often cause unexpected billing
- Storage cost
Regions
The number of global regions directly impacts:
- Application performance
- Latency
- Disaster recovery capabilities
- Compliance with data laws
Current global footprint (2026):
| Cloud Provider | Regions (2026) | Core Strengths & Market Positioning |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Azure | 70+ |
|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | 39+ |
|
| Google Cloud (GCP) | 43+ |
|
More regions mean faster service, greater redundancy, and easier compliance with regulations such as GDPR (Europe), DPDP Act (India), HIPAA (US), and local UAE/UK data laws.
Services
A cloud provider must meet workload demands and support future innovation.
Compare capabilities across:
- Compute services (VMs, serverless, containers)
- Storage (object, block, archive)
- Databases (managed SQL, NoSQL, analytics)
- AI/ML tools
- DevOps and automation
- Big data and analytics
- IoT and edge services
AWS currently offers 200+ services, Azure offers 250+, while GCP leads in AI, analytics, and custom machine types.
Choosing a provider with the right breadth of services ensures your architecture can evolve without migrating platforms later.
Security
Security remains the top concern for cloud-adopting organizations.
Evaluate each provider’s:
DPDP Act (India)
- Encryption (in transit + at rest)
- IAM (Identity and Access Management)
- Key management services
- Network and firewall protections
- Shared responsibility model
Compliance certifications such as:
- ISO 27001
- SOC-2
- GDPR
- HIPAA
- PCI-DSS
Support
A reliable cloud provider must offer strong support and guaranteed uptime.
Key factors to compare:
- Disaster recovery and backup options
- Support tiers (basic, professional, enterprise)
- Live chat, ticketing, and phone support availability
- Access to technical account managers
- SLA commitments, most top providers offer 99.9% to 99.99% uptime
Confused Between AWS, Azure, or GCP?
In 2026, the wrong choice can cost you 30% more in hidden cost and AI compute. TeleGlobal International provides a vendor-neutral Cloud Fit-Gap Analysis to ensure you choose the platform that matches your specific compliance and performance needs.
The top cloud service providers in 2026
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS holds about one third of the global market. It offers over 200 cloud services.
Strengths:
- Largest global network.
- Flexible pricing.
- Enterprise-ready solutions.
Weakness:
- Pricing can be hard to predict.
- Some tools are complex for new users.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure owns around 22 percent share. It fits businesses already using Microsoft tools.
Strengths:
- Smooth integration with Windows and Office.
- Good hybrid cloud options.
- Strong compliance features.
Weakness:
- Pricing can rise quickly.
- Console sometimes feels less clear.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP service)
GCP holds about 12 percent. It is strong in data, AI, and networking.
Strengths:
- Great for analytics and AI.
- Competitive pricing.
- Fast private network.
Weakness:
- Fewer services than AWS or Azure.
- Smaller market presence.
TeleGlobal International
TeleGlobal International is a leading cloud service provider based in Pune, India, with a global footprint. The company delivers end-to-end services across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, helping businesses modernize, migrate, and secure their cloud environments.
Strengths:
- Expertise across multi-cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP).
- Tailored cloud + AI/ML solutions for enterprises.
- Strong presence in consulting, migration, and managed services.
Weakness:
- Smaller global presence compared to hyperscalers.
- Relatively newer brand recognition in the global market
Choosing the Right Cloud Provider by Business Type
Every business has unique cloud needs. Below a clear steps to help organizations select the right cloud provider based on business category, scale, and technology goals.

Startups
Startups need low-cost, scalable, and easy-to-integrate cloud services.
Why GCP?
- One of the most generous free tiers in the industry
- Simple pricing structure to avoid bill shocks
- Strong tools for automation, analytics, and rapid development
Why AWS?
- ideal for early MVPs and prototypes
- Extensive documentation, SDKs, and community support
- Large marketplace of ready-to-use solutions
52% of startups choose AWS for their initial deployment due to flexibility and low entry barriers.
Enterprises
Enterprises require robust security, enterprise integrations, compliance certifications, and global scale.
Why AWS?
- Largest and most mature cloud service portfolio (200+ services)
- Exceptional global reliability and performance
- Industry-leading security and compliance ecosystem
Why Azure?
- Seamless integration with Microsoft tools (Windows Server, Active Directory, Office 365)
- Exceptional hybrid cloud capabilities
- Strong presence in regulated industries (finance, healthcare, manufacturing)
Azure leads enterprise cloud adoption in sectors with deep Microsoft legacy environments.
AI and data
Data-driven and AI-first businesses need advanced analytics, GPU availability, and powerful ML platforms.
Why GCP?
- Best-in-class AI/ML ecosystem—Vertex AI, TensorFlow, TPUs
- BigQuery is one of the fastest large-scale data warehouses
- Superior performance for analytics workloads
- Exceptional pricing for data pipelines and large datasets
Independent benchmarks rank BigQuery as the top-performing cloud data warehouse.
Hybrid IT
Organizations with existing on-prem infrastructure need tight integration between data centers and the cloud.
Why Azure?
- Azure Arc provides unified management across on-prem, multi-cloud, and edge
- Best compatibility with legacy enterprise IT systems
- Strong identity & access integration via Azure Active Directory
Hybrid cloud adoption has increased 58% year-over-year due to compliance and data residency demands.
Global reach
Companies that need global coverage, such as SaaS platforms, BFSI, eCommerce, logistics, and IT & media, depend heavily on low latency, edge presence, and multi-region redundancy.
Why AWS?
- Widest global presence
- 33 regions and 105 availability zones worldwide
- Ultra-low-latency CDN through Amazon CloudFront
- Best suited for multi-region deployments and disaster recovery
AWS maintains the largest global cloud footprint among all providers.
Cloud hosting providers vs cloud storage providers
- Cloud hosting providers manage servers for apps, sites, and workloads.
- Cloud storage providers offer scalable space for files, backups, and archives.
| Feature | Cloud Hosting Providers | Cloud Storage Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Run apps & workloads | Store files & data |
| Resource Type | Compute | Storage |
| Examples | EC2, Azure VM, GCE | S3, Blob, GCS |
| Usage | Websites, APIs, apps | Backups, archives, media |
| Scaling | Scales compute power | Scales storage capacity |
Leaders include AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, and GCP Storage.
Services provided by cloud computing
Cloud providers offer a wide range of services that enable organizations to build, deploy, scale, and secure applications with speed and efficiency. While each platform (AWS, Azure, GCP) names its services differently, the core categories remain consistent across the industry.
According to Gartner, cloud services revenue grew 20.4% to total $675.4 billion in 2024, reinforcing their role as the foundation of digital transformation.
Every cloud services provider offers common tools:
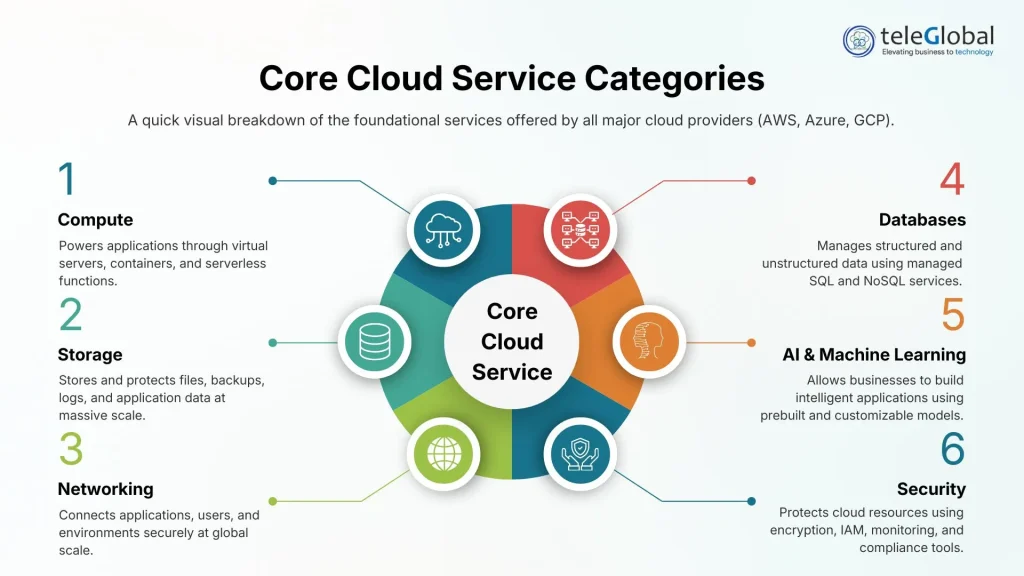
- Compute:
Compute is the backbone of cloud operations, powering applications, workloads, and virtual infrastructure.
Common offerings include:
- Virtual Machines (VMs)
AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine - Containers & Orchestration
Amazon ECS/EKS, Azure AKS, Google GKE - Serverless Computing (Functions)
AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions
Why it matters:
Compute services offer elasticity, enabling businesses to scale applications up or down instantly based on demand.
- Storage:
Cloud storage provides secure, durable, and infinitely scalable infrastructure for files, backups, logs, and business data.
Types include:
- Object Storage
Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage - Block Storage
Amazon EBS, Azure Disk Storage, Persistent Disks (GCP) - File Storage
Amazon EFS, Azure Files, Filestore (GCP)
Object storage such as Amazon S3 offers 99.999999999% durability.
- Networking:
Networking ensures that applications stay fast, secure, and globally accessible.
Key components:
- Load Balancers
- DNS Services (Route 53, Azure DNS, Cloud DNS)
- Firewalls & Security Groups
- Content Delivery Networks (CDN) such as CloudFront, Azure CDN, Cloud CDN
Why it matters:
Networking services enable low latency, traffic distribution, and secure connectivity between cloud and on-premises systems.
- Databases:
Cloud providers offer managed databases that reduce operational overhead, improve performance, and increase reliability.
Types of databases:
- Relational Databases (SQL)
Amazon RDS, Azure SQL, Cloud SQL - NoSQL Databases
DynamoDB, Cosmos DB, Firestore/Bigtable - Data Warehousing
Amazon Redshift, Azure Synapse, Google BigQuery
BigQuery is recognized as one of the fastest analytics engines for real-time data processing.
- AI and ML:
Cloud providers offer powerful AI and ML tools to help organizations build intelligent applications.
Common services:
- Pre-built AI APIs (vision, speech, NLP)
- ML model training platforms
- AutoML tools
- GPU/TPU compute support
Examples:
- AWS SageMaker
- Azure Machine Learning
- Google Vertex AI
Adoption of cloud AI platforms increased 32% year-over-year as companies accelerate automation and analytics.
- Security:
Security is a core pillar of cloud computing, protecting applications, data, and infrastructure.
Key offerings include:
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Identity & Access Management (IAM)
- Key management (KMS)
- Firewalls & Zero Trust architectures
- Compliance tools for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, DPDP Act (India)
Why it matters:
According to IBM, 45% of cloud breaches are caused by misconfigurations, making cloud-native security essential.
These services form the base of all cloud computing providers.
Regional focus
- Cloud service providers in India compete on low cost and free credits.
- In the US, large firms use AWS for scale or Azure for Microsoft ties.
- In the UK, compliance drives adoption. Azure and GCP cover strict rules.
- In the UAE, local support matters for cloud hosting providers.
- In Europe, GDPR shapes which best cloud providers win business.
Why multi-cloud is growing
Many firms now use more than one cloud services provider. It lowers risk and avoids lock-in.
Common setups:
- AWS for compute.
- Azure for hybrid.
- GCP for AI and analytics.
How to test providers
- Use free tiers.
- Check speed in your region.
- Compare management consoles.
- Run pilot projects.
- Review billing reports.
Signs you should switch providers
- Costs keep rising.
- Downtime impacts your users.
- Support is weak.
- Missing needed services.
Conclusion
The right cloud providers choice is vital in 2026. It affects cost, security, and growth.
The best cloud service provider depends on your needs. AWS, Microsoft Azure, and GCP lead the market. Smaller cloud hosting providers and regional players also matter.
We at TeleGlobal help you choose wisely. From cloud storage providers to migration into AWS, Azure, or GCP service, we ensure smooth adoption and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are cloud service providers?
Companies offering computing, storage, and networking over the internet.
2. Who are the top cloud service providers in 2026?
AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Teleglobal International.
3. What do cloud storage providers offer?
They provide scalable storage for data, backups, and apps.
4. Which is the best cloud service provider for startups?
GCP and AWS are best for free credits and simple pricing.
5. Do cloud service providers in India differ from global ones?
Yes. They focus on cost, local data centers, and compliance.
6. What services are provided by cloud computing?
Compute, storage, networking, AI, databases, and security.
7. Can I use more than one cloud services provider?
Yes. Multi-cloud reduces risk and adds flexibility.
8. Who are cloud server providers?
Providers that run virtual servers for apps and hosting.